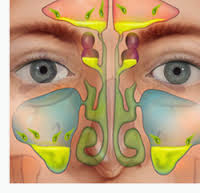
Rhinosinusitis or sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. It can be due to infection, allergy, or autoimmune problems. Most cases are due to a viral infection and resolve over the course of 10 days.
Rhinosinusitis or sinusitis is defined as an inflammation of the mucous membrane that lines the paranasal sinuses and is classified chronologically into several categories:
Nursing Diagnosis for Rhinosinusitis : Ineffective Airway Clearance related to excessive mucus.
NOC :
NIC :
Airway Management
Airway Suction
http://nurse-books.blogspot.com/2015/01/nursing-care-plan-for-ineffective.html
Rhinosinusitis or sinusitis is defined as an inflammation of the mucous membrane that lines the paranasal sinuses and is classified chronologically into several categories:
- Acute rhinosinusitis — a new infection that may last up to four weeks and can be subdivided symptomatically into severe and non-severe;
- Recurrent acute rhinosinusitis — four or more separate episodes of acute sinusitis that occur within one year;
- Subacute rhinosinusitis — an infection that lasts between four and 12 weeks, and represents a transition between acute and chronic infection;
- Chronic rhinosinusitis — when the signs and symptoms last for more than 12 weeks; and
- Acute exacerbation of chronic rhinosinusitis — when the signs and symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis exacerbate, but return to baseline after treatment.
Nursing Diagnosis for Rhinosinusitis : Ineffective Airway Clearance related to excessive mucus.
NOC :
- Respiratory status : Ventilation
- Respiratory status : Airway patency
- Aspiration Control
- Demonstrate effective cough and breath sounds were clean, no cyanosis and dyspnea (able to produce a sputum sample, was able to breathe easily, no pursed lips).
- Indicates that a patent airway (the client does not feel suffocated, the rhythm of breathing, respiratory frequency in the normal range , no abnormal breath sounds).
- Being able to identify and prevent the factors that can inhibit airway.
NIC :
Airway Management
- Open the airway, use techniques chin lift or jaw thrust if necessary.
- Position the patient to maximize ventilation.
- Identification of the patient's need for installation tools artificial airway.
- Installing mayo if necessary.
- Perform chest physiotherapy if necessary.
- Remove secretions by coughing or suctioning.
- Auscultation of breath sounds, note the presence of additional noise.
- Perform suction on the mayo.
- Give bronchodilators if necessary.
- Give humidifier wet gauze, with NaCl moist.
- Set intake to optimize fluid balance.
- Monitor respiration and O2 status.
Airway Suction
- Ensure the needs of oral / tracheal suctioning.
- Auscultation of breath sounds before and after suctioning.
- Inform the client and family about suctioning.
- Ask the client a deep breath before suction done .
- Give O2 by using a nasal, to facilitate nasotracheal suction.
- Use sterile tools every action.
- Instruct the patient to rest and deep breath, after the catheter is removed from the nasotracheal.
- Monitor the status of the patient oxygen.
- Teach the patient's family, how to perform suction.
- Stop suction and administer oxygen if the patient showed bradycardia, increase in O2 saturation, etc.
http://nurse-books.blogspot.com/2015/01/nursing-care-plan-for-ineffective.html