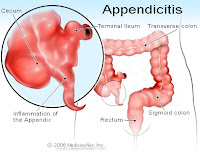
Appendicitis a condition characterized by inflammation of the appendix. It is classified as a medical emergency and many cases require removal of the inflamed appendix, either by laparotomy or laparoscopy. Untreated, mortality is high, mainly because of the risk of rupture leading to peritonitis and shock. Reginald Fitz first described acute and chronic appendicitis in 1886, and it has been recognized as one of the most common causes of severe acute abdominal pain worldwide. A correctly diagnosed non-acute form of appendicitis is known as "rumbling appendicitis".
Etiology
The exact cause of appendicitis is often unclear, but it is commonly associated with the blockage of the appendix. This blockage can occur due to various factors, including hardened stool, enlarged lymphoid follicles, or even tumors. Once the appendix is blocked, bacteria can multiply within it, leading to inflammation and subsequent infection.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of appendicitis is crucial for timely intervention. The condition typically manifests with abdominal pain that starts around the navel and later shifts to the lower right abdomen. This pain often intensifies and may be accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Individuals experiencing these symptoms should seek immediate medical attention, as a ruptured appendix can lead to severe complications.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing appendicitis. Age is a significant factor, with individuals between the ages of 10 and 30 being more susceptible. Additionally, a family history of appendicitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and conditions such as cystic fibrosis can elevate the risk. Gender may also play a role, as males tend to be at a slightly higher risk than females.
Prevention
While appendicitis cannot always be prevented, there are measures individuals can take to reduce their risk. Dietary habits play a crucial role; a diet rich in fiber can help prevent constipation, reducing the likelihood of blockages in the appendix. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy weight are also beneficial in preventing appendicitis.
Prompt treatment of infections in the gastrointestinal tract can minimize the risk of appendicitis, as can addressing conditions that may contribute to blockages. It's essential to listen to the body and seek medical attention if any symptoms indicative of appendicitis arise.
The exact cause of appendicitis is often unclear, but it is commonly associated with the blockage of the appendix. This blockage can occur due to various factors, including hardened stool, enlarged lymphoid follicles, or even tumors. Once the appendix is blocked, bacteria can multiply within it, leading to inflammation and subsequent infection.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of appendicitis is crucial for timely intervention. The condition typically manifests with abdominal pain that starts around the navel and later shifts to the lower right abdomen. This pain often intensifies and may be accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Individuals experiencing these symptoms should seek immediate medical attention, as a ruptured appendix can lead to severe complications.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing appendicitis. Age is a significant factor, with individuals between the ages of 10 and 30 being more susceptible. Additionally, a family history of appendicitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and conditions such as cystic fibrosis can elevate the risk. Gender may also play a role, as males tend to be at a slightly higher risk than females.
Prevention
While appendicitis cannot always be prevented, there are measures individuals can take to reduce their risk. Dietary habits play a crucial role; a diet rich in fiber can help prevent constipation, reducing the likelihood of blockages in the appendix. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy weight are also beneficial in preventing appendicitis.
Prompt treatment of infections in the gastrointestinal tract can minimize the risk of appendicitis, as can addressing conditions that may contribute to blockages. It's essential to listen to the body and seek medical attention if any symptoms indicative of appendicitis arise.
Nursing Diagnosis for Nursing Care Plan Appendicitis
Activity intolerance related to limitation of motion secondary to pain.
Activity Intolerance is used when a patient has insufficient physiological or psychological energy to endure or complete required or desired daily activities.
Most activity intolerance is related to generalized weakness and debilitation secondary to acute or chronic illness and disease. Activity intolerance may also be related to factors such as obesity, malnourishment, side effects of medications, or emotional states such as depression or lack of confidence to exert one’s self. Nursing goals are to reduce the effects of inactivity, promote optimal physical activity, and assist the patient to maintain a satisfactory lifestyle.
Activity tolerance
Expected Result:
Clients can move without restriction
Nursing Intervention and Rational :
- Note the emotional response to mobility.
R / immobilization imposed will increase anxiety. - Provide activities in accordance with client's circumstances.
R / Increasing organ kormolitas sesuiai expected. - Give the client for passive motion exercises and active movements.
R / Improve body mechanics. - Assist clients in conducting activities that are burdensome.
R / Avoiding things that can aggravate the situation.
Bibliography
1. Bhangu, A., Søreide, K., Di Saverio, S., Assarsson, J. H., Drake, F. T., & SOS collaborative. (2015). Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. The Lancet, 386(10000), 1278-1287.
2. Vons, C., Barry, C., Maitre, S., Pautrat, K., Leconte, M., Costaglioli, B., ... & French Surgical Association. (2011). Amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid versus appendicectomy for treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 377(9777), 1573-1579.